
The EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve is a device used to reduce diesel engine emissions. It can send part of the exhaust gas back into the intake passage, thereby reducing the generation of nitrogen oxides (NOx). In modern diesel engines, electronically controlled EGR valves have become mainstream.
In this article, we will give you a detailed introduction to vacuum operated EGR valves (also called pneumatic EGR valves) and electronically controlled EGR valves (also called electric EGR valves).
1. Vacuum Operated EGR Valves
1.1 Vacuum Operated EGR Valve System Components
The figure below shows the system layout of the vacuum operated EGR valve. The EGR position sensor feeds back the current EGR valve opening degree to the ECU. The ECU calculates the current EGR rate based on the opening degree, thereby controlling the duty cycle of the EGR vacuum regulator (EGR solenoid valve, EGR vacuum valve, EGR vacuum solenoid valve).

The ECU determines the EGR rate based on the sensor signal, and determines the duty cycle of the pulse signal in the EGR vacuum regulator. The greater the duty cycle, the longer the opening time of EGR vacuum regulator, and the greater the vacuum degree of the vacuum valve, the EGR valve opening degree, and the EGR rate; On the contrary, the smaller the duty cycle of the pulse signal, the smaller the EGR rate.
What is the duty cycle signal? To put it simply, for example, there are 24 hours in a day, and you sleep for 12 hours. Then the duty cycle of sleeping is 1/2=50%. And if you sleep for 8 hours, the duty cycle is 1/3.
1.2 How the Vacuum Operated EGR Valve Works
The working principle of the vacuum operated EGR valve is as follows:
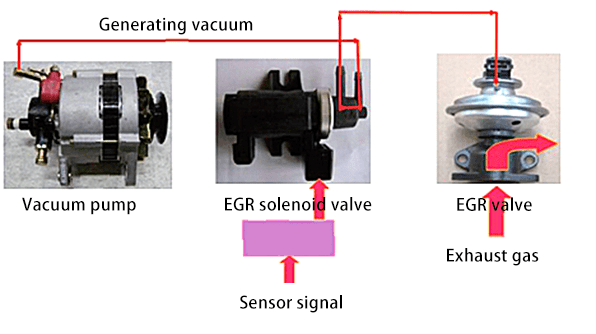
The vacuum pump is generally installed behind the generator. When the generator is working, it drives the vacuum pump to work and generate a negative pressure of 0.75kPa. The EGR vacuum regulator (EGR solenoid valve) is an electromagnetic high-frequency switching valve controlled by an ECU. When the solenoid coil is energized, the vacuum valve is turned on and the EGR valve opens.

1.3 Vacuum Operated EGR Valve Types
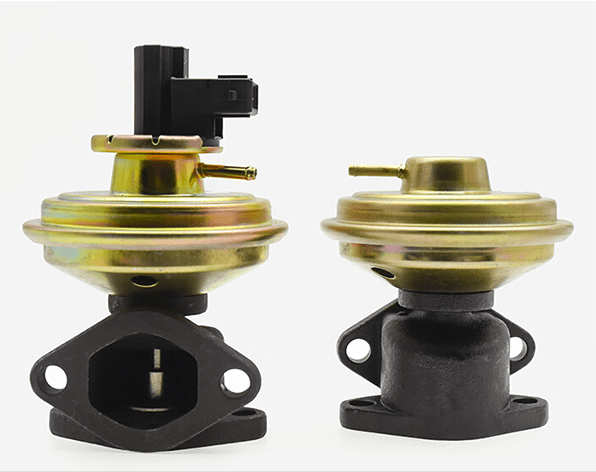
Vacuum operated EGR valves are divided into those with a position sensor and without a position sensor. The EGR valve with a position sensor is a five-wire type, and the EGR valve without a position sensor is a two-wire type.
2. Electronically Controlled EGR Valves
2.1 Electronically Controlled EGR Valve System Components
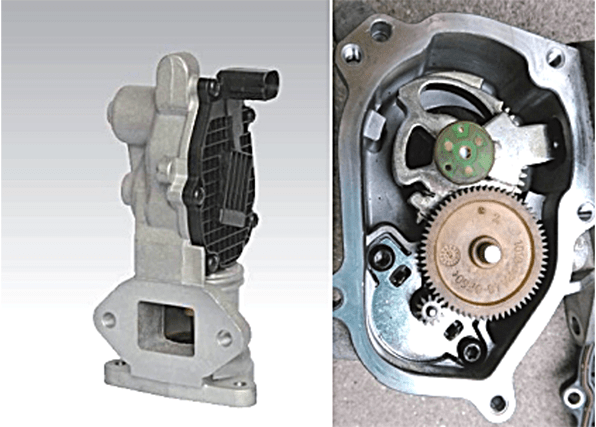
The electronically controlled EGR valve is a linear EGR control valve and a proportional solenoid valve controlled by a duty cycle signal. During operation, the electronic control unit determines the EGR amount according to the operating conditions, and then determines the duty cycle based on the pre-calibration condition to control the amount.
Because the temperature of the exhaust gas is too high and directly entering the cylinder will cause very poor combustion, resulting in insufficient power and black smoke, the exhaust gas must be cooled before it can enter the cylinder. This is where an EGR cooler is used.

The cooling process and principle are as follows:
(1) The return exhaust gas flows in from the gas inlet end, passes through the cooling pipes, achieves heat exchange, and then flows out from the gas outlet end (shown by the red arrows).
(2) The cooling water enters the cooler from the water inlet, passes through the outside of the cooling pipes, absorbs heat, and then flows out from the water outlet (shown by the blue arrows).

This kind of valve is usually equipped with an opening degree sensor (position sensor), which feeds back the actual valve opening degree to the electronic control unit to achieve closed-loop control of the valve opening degree, thereby achieving precise control of the EGR amount. Therefore, its control accuracy and response speed is higher than that of vacuum operated EGR valves.
At present, this kind of solenoid valve is used in more and more applications. Because it is close to high-temperature gas and has a poor working environment, it has higher reliability requirements.
Electronically controlled EGR valves are generally the five-wire type. For example, Cummins CM2220 is equipped with an EGR system, and its pin definitions are as follows:

|
Pin |
Definition |
Open-circuit voltage |
|
A05 |
Motor control line+ |
24V |
|
A29 |
Motor control line- |
24V |
|
A90 |
Sensor power line |
5V |
|
A96 |
Sensor signal line |
5V |
|
A66 |
Sensor ground wire |
0V |

2.2 How the Electronically Controlled EGR Valve Works
The working principle of the electronically controlled EGR valve is as follows:

When the engine is running, the control module will determine whether the EGR valve needs to be opened based on the engine load, speed and other parameters. If it needs to be opened, the control module sends a signal to open it.
After the EGR valve is opened, part of the exhaust gas will be pumped back into the intake passage, and then enter the combustion chamber after being mixed with fresh air. This can reduce the temperature and pressure within the combustion chamber, thereby decreasing NOx production.
The opening and closing of the electronically controlled EGR valve is achieved by an electromagnet. When the control module sends a signal, the electromagnet is energized, causing the EGR valve to open. When the control module stops sending signals, the solenoid is de-energized and the EGR valve closes.


