
The solenoid valve is a component that controls the position of the valve core through an electromagnetic coil to open, close and change the flow direction of the medium (air, hydraulic oil, etc.) in the pipeline. It usually consists of a valve body, valve core, solenoid coil, spring and base.
Solenoid valves are widely used in automation control systems, industrial production, petrochemical and other fields. They have the advantages of simple structure, fast response speed and high reliability.
Before delving into various solenoid valve symbols, it is necessary to understand the types of solenoid valves.
1. Solenoid Valve Types
Solenoid valves can be divided into three categories according to their working principles: direct-acting, pilot-operated, and semi-direct acting.
According to the number of working positions and ports of the solenoid valve, the solenoid valve can be divided into two-position two-way, two-position three-way, two-position four-way, two-position five-way, etc.
According to the number of solenoid coils, solenoid valves can be divided into two types: single coil and double coil. 2-position 2-way and 2-position 3-way solenoid valves are generally single coil type, while 2-position 4-way, 3-position 4-way, and 2-position 5-way can be single coil type or double coil type.
The power supply voltages of solenoid valves include 220V, 110V, and 24V. They can also be divided into explosion-proof and non-explosion-proof solenoid valves.
2. Graphic Symbols of Various Types of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves have a wide range of uses, and their symbols vary slightly due to different industries.
Process Industry
On the piping and instrumentation diagram (P&ID or PID) in the process industry, the graphical symbol of the solenoid valve is as shown below:
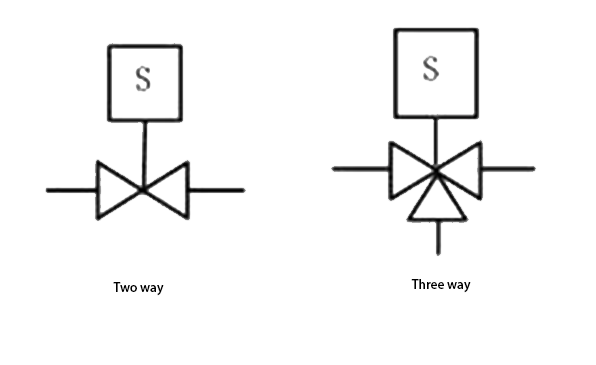
Machinery Industry
In the mechanical industry or mechatronic transmission systems (pneumatic or hydraulic systems), the graphical symbols used for solenoid valves are as shown in the figure below and they respectively represent a two-position two-way and two-position three-way solenoid valves.
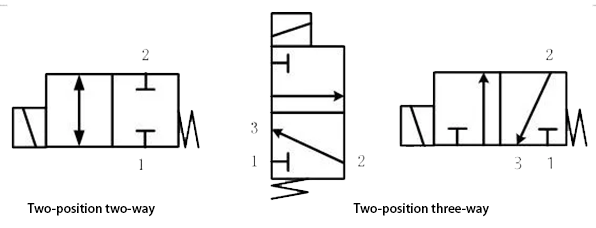
1 Air inlet, 2 Working port, 3 Exhaust port
●In the graphic symbols, the number of boxes indicates that of "positions".
●The arrow in the box indicates that the fluid at two ports is connected.
●The ┫-shaped symbol in the box indicates that the port is closed.
●The number of intersection points in a box indicates how many "ways" (ports) there are.
● Based on the above, there are usual two-position two-way, two-position three-way, two-position four-way, and two-position five-way solenoid valves.
Each directional control valve has two or more working positions.
2.1 Direct Acting Solenoid Valve
The electromagnetic force is used to push the valve core and achieve the flow direction change. When the coil is energized, the valve opens and fluid can pass through. When the coil is de-energized, the valve closes and fluid cannot pass through.
The symbol in the figure below indicates that the solenoid valve is a direct-acting type.

2.3 2/2 Solenoid Valve
Two positions means that the valve core works in two states. When the coil is not energized, the valve core is in one position. When the coil is energized, the valve core moves to the other position. By changing the valve core position, the opening or closing state of the valve is switched. Two-way means that the valve has two ports (one inlet and one outlet).
The two-position two-way valve is actually a stop valve, which serves the purpose of closing / opening the fluid in the pipeline and has no direction change function. The true directional control valve is a two-position five-way or three-position five-way valve.

2.4 3/2 Solenoid Valve
The figure below shows a direct-acting two-position three-way solenoid valve. The solenoid valve has 2 positions and 3 ports.

4/2 Solenoid Valve
The figure below takes a two-position four-way hydraulic solenoid valve as an example.

2.5 5/2 Solenoid Valve
The figure below shows a two-position five-way pneumatic solenoid valve. Two-position refers to two working positions, and five-way refers to one air inlet, two working ports, and two exhaust ports. Single coil and double coil types are available.
Single coil two-position five-way solenoid valve

Double coil two-position five-way solenoid valve

2.6 4/3 Solenoid Valve
The three-position four-way directional control valve means that the valve has three working positions and four ports. P is the oil inlet and T is the oil return. Ports A and B are respectively connected to the upper and lower chambers of the actuator.

2.7 5/3 Solenoid Valve
As the name suggests, a three-position five-position valve has three working positions and five ports. There is no single coil three-position five-way valve, but only dual coil type.



