
The solenoid valve is an industrial electromagnetic device used to adjust the direction, flow, speed, etc. of the medium. You may have some doubts about how to select a solenoid valve, so today we would like to share something relevant with you. The following article will introduce in detail the process and key points of solenoid valve selection to help you better complete the selection task.
1. Importance of Correct Solenoid Valve Selection
Solenoid valve selection is a very important part of the industrial automation control system. Its correct selection can not only ensure the stable operation of the system, but also improve the reliability and efficiency of the equipment. Solenoid valve selection involves many aspects, including working environment, control requirements, fluid characteristics, etc.
2. Factors to Consider for Solenoid Valve Selection
Solenoid valve selection should consider six on-site working condition requirements, namely pipe diameter, fluid properties, pressure level, power supply voltage, operation mode, and working environmental requirement.
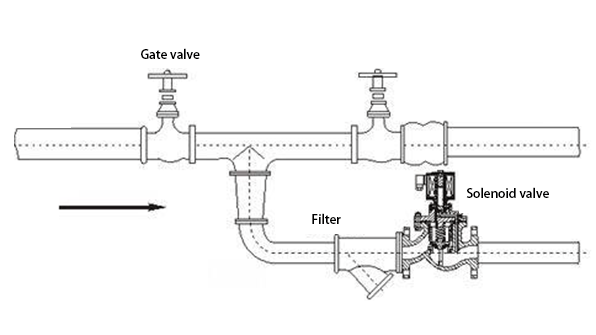
2.1 Pipe Diameter
According to the pipeline diameter, select the solenoid valve diameter size (i.e. DN), and connection method (there are usually two common connection methods for solenoid valves, flange connection and threaded connection).
(1) Determine the valve diameter size (DN) according to the on-site pipeline inner diameter size;
(2) Generally choose flange connection if DN>50. If 25≤DN≤50, you can freely choose threaded or flange type connection according to your needs. If DN≤25, choose threaded connection.
2.2 Fluid Properties
Select the solenoid valve body material, sealing material, etc. according to the fluid properties.
(1) Corrosive Fluid: The valve body material should be stainless steel or PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), and fluororubber or PTFE sealing materials should be selected;
(2) Edible or Ultra-Clean Fluid: The valve body should be made of sanitary stainless steel and equipped with silicone rubber sealing material;
(3) High-Temperature Fluid: Choose a solenoid valve made of high-temperature resistant materials, and choose appropriate sealing materials;
(4) Fluid State: There are roughly gaseous, liquid or mixed states. Especially when the valve diameter is larger than DN25, you must be distinguish the fluid state when ordering;
(5) Fluid Viscosity: If it exceeds 50cSt, a high viscosity solenoid valve needs to be selected.
(6) Fluid Cleanliness: When the medium contains a small amount of tiny impurities, a diaphragm type solenoid valve can be selected, but you can also choose other types when a filter is installed in front of the solenoid valve.
(7) Flammable Fluid: Use intrinsically safe explosion-proof solenoid valves and explosion-proof solenoid valves.

2.3 Pressure Level
Select the solenoid valve working principle and structure type according to the pressure level.
(1) Nominal Pressure: This parameter has the same meaning as other general valves’, and is determined based on 1.5 times the nominal pressure of the pipeline or the operating pressure;
(2) Working Pressure Difference: It refers to the value obtained by subtracting the pipeline pressure at the rear end of the valve from that at the front end of the valve when the solenoid valve is in a closed or open state. When there is no pressure difference, low pressure difference, or vacuum state, direct acting or semi-direct acting type valves must be selected. When there is a certain pressure difference (0.04Mpa) or above, various principles and structures (direct-acting, semi- direct acting, or pilot-operated) can be selected.
2.4 Power Supply Voltage
Power supply voltage selection: Generally, there is DC12V, DC24V, AC24V, AC110V, AC220V, and AC380V available.
2.5 Valve Opening or Closing Time or Special Needs (Valve Operation Type)
Select the control method according to the opening and closing time of the solenoid valve or special needs: normally closed, normally open, self-holding, emergency shut off (manual reset).
(1) When the solenoid valve needs to be opened for a long time, and the continuous opening time greatly exceeds the closing time, the normally open type should be selected.
(2) If the valve opens and closes frequently, or the opening time is short or the opening and closing times are about the same, choose the normally closed type.
(3) However, some solenoid valves are used for safety protection in some working conditions, such as kiln flame monitoring, gas leakage alarms, and fire alarm and linkage control systems, emergency shut-off solenoid valves should be selected.
(4) Self-holding solenoid valve (also known as: bistable solenoid valve) adopts a new technology, mainly used in applications where energy saving or low-voltage driving is required.

2.6 Working Environmental Requirement
Choose auxiliary functions according to environmental requirements: explosion-proof, non-return, manual, waterproof, fog-proof, and submersible, etc.
(1) When the solenoid valve needs to work in inflammable and explosive environments, select the explosion-proof one;
(2) When there is backflow of the pipeline medium, a solenoid valve with a non-return function can be selected;
(3) When on-site manual operation of the solenoid valve is required, one with manual function can be selected;
(4) Waterproof and dustproof types (IP rating above IP45) should be selected for outdoor installation or dusty applications. If used in fountains or underwater pipelines, a submersible solenoid valve (IP rating above IP68) must be used.

3. Solenoid Valve Ordering Instructions
1. When ordering, please indicate the model, nominal diameter, nominal pressure, working medium, working pressure difference, medium temperature, power supply voltage, and medium viscosity.
2. If the working voltage of the solenoid valve is not a common voltage, which can be specially ordered. Please indicate the voltage fluctuation when ordering.
3. Please specify, if the valve needs to be opened for up to 12 hours or energized for a long time. Of course, if there are flammable and explosive materials in the working environment, please choose an explosion-proof solenoid valve.
4. Summary of Basic Steps for Solenoid Valve Selection

1. Determine the control object: First, it is necessary to clarify the control object of the solenoid valve, such as gas, liquid, etc. Different media have different requirements for solenoid valves, which need to be selected according to the actual situation.
2. Determine the working pressure: The working pressure of the solenoid valve should match that of the system. Too high or too low pressure may cause the solenoid valve to not work properly.
3. Determine the diameter and flow rate: Select the appropriate diameter and flow rate according to the flow requirements of the system. Too large or too small diameter may affect system performance.
4. Determine the action type: The operation types of solenoid valves include direct-acting, semi-direct acting and indirect-acting (pilot-operated). Choose the appropriate operation type according to the control requirements.
5. Select the solenoid valve type: There is two-position three-way, two-position five-way, etc. available.
6. Determine the connection method: The connection methods of the solenoid valve include flange connection, threaded connection, etc. Select the appropriate solenoid valve connection method according to the pipe connection method of the system.
7. Determine the protection level: Select the appropriate protection level according to the working environment to ensure that the solenoid valve can work normally in harsh environments.


