Hydraulic systems are widely used. Why do we use them? What is the working principle of them? This article uses simple pictures and texts to help you understand the components, working principle, advantages, disadvantages and applications of the hydraulic system.
1. What Is a Hydraulic System
A hydraulic system uses liquid as the working medium, converts the mechanical energy of the prime mover into the pressure energy of the liquid (hydraulic energy) through the driving device, and then converts it into mechanical energy through the pipeline, hydraulic control and regulating device, etc. with the help of the actuator to drive the load to achieve linear or rotary motion.
2. Why We Use a Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system converts energy from mechanical energy to hydraulic energy and then to mechanical energy. It seems unnecessary.
But almost all machinery or machines require transmission mechanisms. This is because it is generally difficult for the prime mover to directly meet the requirements of the actuator in terms of speed, force, torque or movement mode, and an intermediate link - the transmission device is needed to adjust and control them. Hydraulic transmission is one type of the adjusting and controlling methods.
Other transmission methods include:
●Mechanical transmission: Commonly used parts are gears, crankshafts, shafts, belts, etc.
●Pneumatic transmission: Air or other gases are commonly used as transmission medium.
●Electric transmission: Commonly used parts are DC motors, thyristors, AC motors, frequency converters, etc.
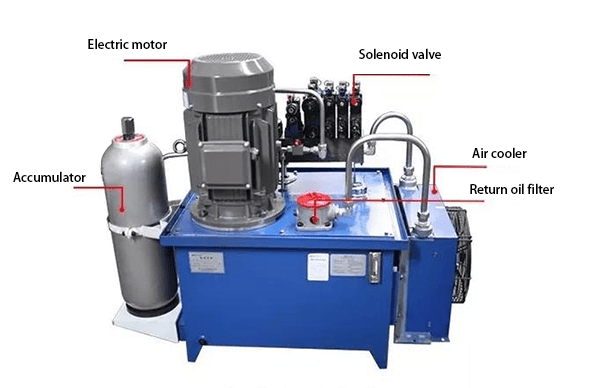
3. What Are Basic Components of a Hydraulic System

3.1 Power Component
In a hydraulic system, the power component refers to the hydraulic pump, which converts the mechanical energy input by the prime mover into the hydraulic energy. Its function is to provide pressurized oil for the hydraulic system, and it is the power source of the system.
3.2 Actuator
The actuator refers to a hydraulic cylinder or hydraulic motor, which is a device that converts hydraulic energy into mechanical energy. Its function is to output force and speed (or torque and rotational speed) driven by pressurized oil to drive working parts.
3.3 Control Component
Control components include various valves, such as relief valves, throttle valves, solenoid operated directional control valves, etc. The function of them is to control the pressure, flow rate and flow direction of oil in the hydraulic system to ensure that the actuator completes the expected work.

3.4 Auxiliary Component
Auxiliary components include oil tanks, oil pipes, filters, various indicators and control instruments, etc. Their role is to provide the necessary conditions for the system to work properly and facilitate monitoring and control of it.
3.5 Working Medium
The working medium is the transmission fluid, usually called hydraulic oil, through which the hydraulic system achieves movement and power transmission.
4. How a Hydraulic System Works
The working principle of a hydraulic system can be simply summarized as follows: The hydraulic pump sucks oil from the tank, and sends it to the hydraulic valve through pressure. The hydraulic valve controls its flow direction and pressure, and then sends it to the hydraulic cylinder (or hydraulic motor), which converts the hydraulic energy into mechanical energy to complete the corresponding work.

5. Pros and Cons of Hydraulic Systems
5.1 Advantages of Hydraulic Systems
1. Able to output large thrust or large torque.
2. Able to easily achieve stepless speed regulation, with a large speed regulation range, and available for speed regulation during the system operation.
3. Under the same power conditions, the hydraulic system is small in size, light in weight, compact in structure, and has great flexibility in layout and installation.
4. The system can make the movement of the actuator very uniform and stable. And because of its fast response speed, frequent direction change can be achieved.
5. Simple operation, convenient adjustment and control, and easy to realize automation.
6. The hydraulic system is easy to achieve overload protection and is safe and reliable to use. Since the moving parts in each hydraulic component work in oil, they can lubricate themselves and have a long service life.
7. Hydraulic components are easy to achieve serialization, standardization and generalization, and are convenient for design, manufacturing, maintenance and promotion.
5.2 Disadvantages of Hydraulic Systems
1. Oil leakage and liquid compressibility will affect the accuracy of the actuator movement, which can not guarantee a strict transmission ratio.
2. It is sensitive to changes in oil temperature and should not work under very high or very low temperature conditions.
3. The energy loss (leakage loss, overflow loss, throttling loss, friction loss, etc.) is large, the transmission efficiency is low, and it is not suitable for long-distance transmission.
4. When a system failure occurs, it is difficult to find the cause.
6. Application of Hydraulic Systems

7. Conclusion
The mutual cooperation of hydraulic system components achieves the movement and operation of mechanical devices. Through reasonable design and selection of hydraulic components, the efficiency and reliability of the hydraulic system can be improved, thereby achieving efficient and safe production and work. At present, the system is widely used in engineering machinery, aerospace, metallurgy, petrochemical and other fields.
Moreover, the advantages of hydraulic transmission are prominent, and its shortcomings will be gradually overcome with the development of science and technology. The development prospects of hydraulic transmission technology are very broad.


