
Figure 1: Ball linear guideway.
Linear guideways are often referred to as guides for short, and their function is to support and guide moving parts for linear reciprocating motion along a given trajectory and stroke. The guide rail is composed of two relatively moving parts, one part is fixed on the frame, called the fixed rail, and the other moves on the fixed rail, called the moving rail.
According to different constructions and working principles, linear guideways can be classified into rolling and sliding (plain) linear guideways.
Rolling linear guideway is moved by steel balls between the slider and the slide rail, so that the load platform can easily move linearly along the slide rail with high precision. But for sliding linear guideways, there are no steel balls between the surfaces. The characteristic of the sliding guide is that a medium is used between the guide and the sliding part, and the types of the medium include solid anti-friction materials, oil and air.

Figure 2: Sliding guideway.
The most distinct differences between the two linear guideways will be introduced as follows.
Friction
Compared with the sliding guideway, the contact part of the rolling guideway is smaller, and it is rolling friction. Thus, the rolling guideway has significantly smaller friction coefficient, so its wear of the components is smaller, too, largely increasing its service life.
Except for the first time, the rolling guideway only needs a small amount of lubricating oil to meet the requirements of use. Under normal circumstances, the lubricating oil replenishment cycle is 1 month, and the running length is about 100Km, and the sliding guide rail may be replenished every ten to fifteen days.
Motion Speed
The rolling guideway is ideal for high-speed motions, because it is less likely to generate frictional heat than the sliding guideway, so its amount of thermal deformation is small. Relevant experiments show that the maximum usage speed between the two differs by more than 10 times.
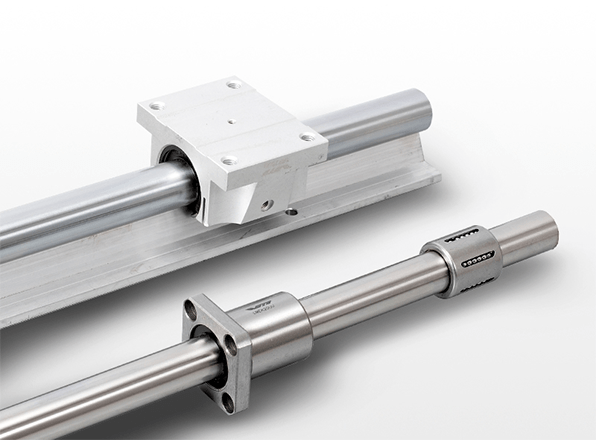
Figure 3: Tuli linear bushing and shafts.
Service Life
As mentioned above, the rolling guideway has smaller friction, and thus, its wear is relatively lighter, too, making its service life to outperform the sliding guideway. What’s more, the fact that the rolling guide adopts steel ball roller technology, with the bearing to be in complete rolling, and that the clearance accuracy can be adjusted also increase the service life of the rolling guideway.
Shock Load Withstanding
But the rolling guideway is not without disadvantages. One of the perspectives from which the rolling guideway cannot hold a candle to the sliding guideway is that the latter can withstand shock loads and vibrations without significant damage to the surfaces.
The table below show a comparison of the pros and cons of the two guideways in details.
| Types | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Rolling guideway | Low coefficient of friction, high sensitivity, stable motion, not prone to crawling, high positioning accuracy, long service life | Poor performance in shock loads and vibrations withstanding |
| Sliding guideway | High load capacity, rare catastrophic failure | Large wear, relative short service life, frequent lubricating requirement |
Figure 4: Comparison of the pros and cons of rolling and sliding linear guideways.
Related Info
How to Calculate the Service Life for Linear GuidewaysHow to Deal with the Abnormal Noises from the Linear Guideways?
Top 7 Linear Guideway Brands
How to Maintain a Linear Guideway?
The Lubrication of the Linear Guideway


