
Figure 1: Refrigeration compressor.
We know that whether it is an air conditioner or a refrigerator, a powerful compressor is needed to ensure its normal and efficient operation. The compressor is the core component of the refrigeration system. Refrigeration equipment using advanced technology and high-quality compressors will prolong the service life, improve the cooling effect, and reduce energy consumption and noise.
1. What Are the Basic Components of a Compression Refrigeration System?
In the vapor compression refrigeration system, the evaporator, compressor, throttling mechanism and condenser are indispensable components, collectively referred to as the four major components of the refrigeration system.
1.1 Evaporator
The evaporator is a heat exchange device. The refrigerant liquid absorbs heat and vaporizes in the evaporator, which produces a cooling effect on the surrounding environment (object) in the process.
The vaporization process of the refrigerant in the evaporator is a boiling process under constant pressure, and the boiling temperature is the saturation temperature under the pressure, that is, the boiling point. Therefore, it is more accurate to call the evaporator a "boiler", but it is customary to call it an evaporator in refrigeration engineering.
The pressure when the refrigerant boils in the evaporator is called the evaporation pressure, the corresponding saturation temperature (boiling point) is called the evaporation temperature, and the boiling vaporization process is called the evaporation process.

Figure 2: Refrigeration system diagram.
1.2 Compressor
A compressor is a device that draws refrigerant vapor from the evaporator and compresses it.
Its functions are:
(1) Sucking out steam from the evaporator to maintain a certain pressure in the evaporator, and at the same time maintaining a certain evaporation temperature;
(2) Compressing the drawn refrigerant vapor, in other words increasing the pressure of the vapor, so that making it possible to condense the refrigerant vapor into liquid at a higher temperature, and the refrigerant can be reused;
(3) Playing the role of transporting refrigerant in the refrigeration system.
1.3 Condenser
The condenser is also a heat exchange device in which the refrigerant condenses and releases heat. The heat is carried away by air or water. The medium used in the condenser to cool the refrigerant vapor and take away the heat released during condensation is called "coolant" or "cooling medium".
The condensation process in the condenser is an isobaric process, in which the refrigerant pressure is called the condensation pressure, and the corresponding saturation temperature is called the condensation temperature.
1.4 Throttling Mechanism
The functions of the throttling mechanism are:
(1) Transforming the condensing agent liquid under the condensing pressure (high pressure) into that under the evaporation pressure (low pressure), creating conditions for the refrigerant to vaporize at low pressure and low temperature;
(2) Adjusting the supply of refrigerant liquid injected into the evaporator.
The throttling mechanism can be an automatic or manual throttle valve (also known as an expansion valve) or a capillary tube.
Vapor compression refrigeration system must have four major components - evaporator, compressor, condenser and throttling mechanism, all of which are indispensable. Of course, an actual refrigeration system is far more than the above four components, and there are also valves and other auxiliary equipment and mechanisms to ensure the safe, reliable and efficient operation of the system.

Figure 3: Refrigeration system.
2. The Role of Refrigeration Compressors in Refrigeration Systems
Connect the above equipment in turn with pipelines to form a closed system. When the system is working, the role of the compressor in the refrigeration system is to suck the low-temperature and low-pressure steam from the evaporator, compress it to increase its pressure and temperature, and discharge the high-temperature and high-pressure steam into the condenser to release heat.
The condensed refrigerant liquid becomes a low-temperature and low-pressure gas-liquid mixture through throttling, which enters the evaporator to absorb heat and becomes a low-temperature and low-pressure steam, and then it is drawn into the compressor to be compressed, thereby forming a cycle and realizing refrigeration.
For the vapor compression refrigeration cycle, the compressor is the key component of the system and the heart of the refrigeration system. The quality of the compressor directly affects the quality of the refrigeration system. Conversely, the design and matching of the refrigeration system determine the working status of the compressor.
The role of compressors in various refrigeration, for example air-conditioning systems, is exactly the same. The only difference is that due to various temperature and cooling capacity requirements, the working conditions and capacity of the compressors are different, forming a variety of refrigeration compressors, such as refrigeration compressors for refrigerators, refrigeration compressors for air conditioners, refrigeration compressors for chillers, etc.
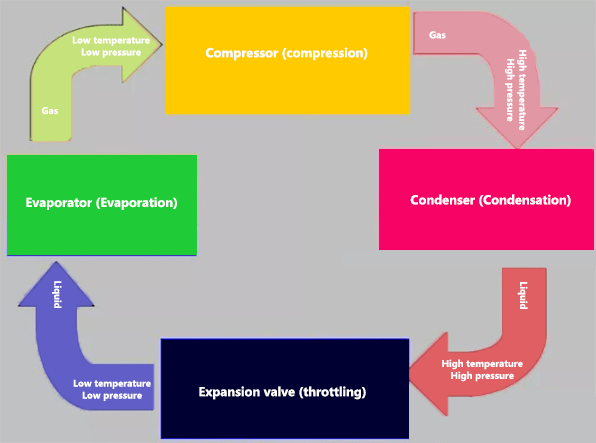
Figure 4: Refrigeration cycle diagram.
The role of the refrigeration compressor is summarized as follows:
1) Drawing refrigerant vapor from the evaporator to ensure a certain evaporation pressure in the evaporator.
2) Increasing the pressure to compress low-pressure and low-temperature refrigerant vapor into high-pressure and high-temperature superheated vapor to create conditions for condensation at higher temperatures (such as temperatures around 35°C in summer).
3) Transporting and pushing the refrigerant to flow in the system to complete the refrigeration cycle.
3. Summary
The compressor is a driven fluid machine that lifts low-pressure gas into high-pressure gas, and is the heart of the refrigeration system. It draws low-temperature and low-pressure refrigerant gas from the suction pipe, compresses the gas through the operation of the electric motor, and discharges high-temperature and high-pressure refrigerant gas to the exhaust pipe to provide power for the refrigeration cycle, thereby realizing refrigeration cycle of compression → condensation (heat release) → throttling → evaporation (heat absorption).
In the refrigeration system, the compressor plays the role of compressing and transporting the refrigerant gas. If there is no compressor, the refrigeration system will not be able to work and circulate normally to achieve refrigeration.
Related Info
5 Types of Compressors for Central AC (Working Principles, Pros and Cons)Mitsubishi vs. Daikin vs. Hitachi vs. Toshiba: Which is the Best Central Air Conditioner Brand?
What is a VRV Air Conditioning System
How to Change Air Compressor Oil (5 Steps)
What are the 4 Main Components in a Central AC System


