
The solenoid valve is a fluid control device, usually used in automatic control circuits. It is actually an "automatic switch" that uses an electrical signal with a smaller current and voltage to control the opening and closing of the fluid pipeline.
Solenoid valves are widely used in all aspects of the automatic control field because of their significant features such as low cost, small size, fast switching speed, simple wiring, low power consumption, and high cost performance.
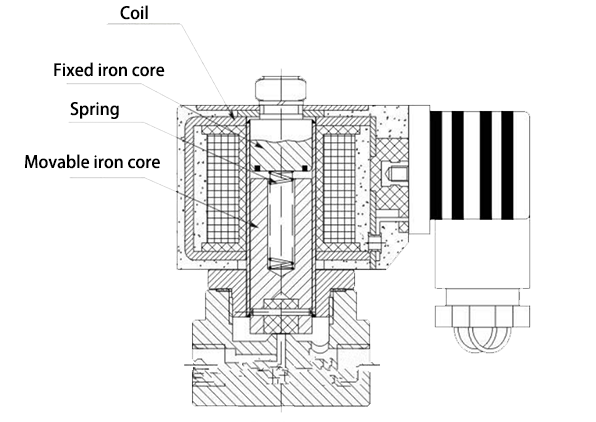
1. Structure of Solenoid Valve
The valve body of the solenoid valve is enclosed in a sealing tube and consists of a spool valve core, a spool valve sleeve, a spring base, etc. The electromagnetic components of the solenoid valve are composed of fixed iron core, movable iron core, coil and other components. The solenoid coil is directly installed on the valve body. In this way, the valve body part and the electromagnetic part form a simple and compact assembly.
2. Types of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves can be divided into many types according to different classification standards.
2.1 Classification According to Working Principle
1. Direct-acting solenoid valve: Its working principle is to use the magnetic force generated by the coil to directly push the movement of the valve core to control the on and off of the fluid. It has a simple structure and fast response speed, but its working pressure range is narrow, generally suitable for low pressure and small flow applications.
2. Pilot operated solenoid valve: It is composed of a pilot valve and a main valve. The pilot valve opens or closes first to control the opening or closing of the main valve by the pressure difference at both ends of the main valve core. It has a large working pressure range and flow adjustment capability, and is suitable for high-pressure and large-flow applications.
3. Semi-direct acting solenoid valve: It combines the characteristics of direct-acting and pilot-operated solenoid valves. When the coil is energized, the pilot valve acts first to balance the pressure at both ends of the main valve core, and then the main valve core acts. This kind of solenoid valve is suitable for applications with large pressure differences and has a wide working pressure range.
3. Diaphragm type solenoid valve: It uses the elastic deformation of the diaphragm to control the on and off of the fluid. It has the advantages of simple structure, fast response speed, and good sealing performance, widely used in the control of liquids, gases and other media.

2.2 Classification According to Valve Body Structure
Solenoid valves can be divided into various types such as stop valves, safety valves, reversing valves, and pressure reducing valves.
1. Stop solenoid valve: It is a commonly used solenoid valve that controls the opening and closing of the fluid channel through the up and down of the valve core.
2. Safety solenoid valve: When the system pressure exceeds the specified value, this valve opens and discharges part of the gas/fluid from the system into the atmosphere or outside the pipeline so that the system pressure does not exceed the allowable value, thereby ensuring that no accident happens in the system due to excessive pressure.
3. Solenoid operated directional control valve: It is a solenoid valve that can change the direction of fluid flow, and is widely used in applications where the direction of fluid needs to be changed.
4. Pressure reducing valve: It is a solenoid valve used to reduce fluid pressure, which adjusts the fluid pressure by controlling the displacement of the valve core to meet different process requirements.
2.3 Classification According to Application Areas
1. Solenoid valve for liquid: It is mainly used to control the on and off of liquid media, such as water, oil, acid liquid, alkali liquid, etc. It has the characteristics of good sealing, corrosion resistance, and high pressure resistance, and is widely used in water treatment, petrochemical, food processing and other industries.
2. Gas solenoid valve: It is mainly used to control the on and off of gas media, such as air, nitrogen, oxygen, etc. It has the advantages of fast response, precise control, and explosion-proof, and is widely used in industrial automation, aerospace, gas equipment and other fields.
3. Steam solenoid valve: It is used to control the on-off of steam medium and has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, high pressure resistance and corrosion resistance. Steam solenoid valves are widely used in heating, printing and dyeing, pharmaceutical and other industries.

2.4 Classification According to Valve Working Modes
Solenoid valves are divided into two types: normally closed type and normally open type according to the working mode of the valve. The normally closed type means that the valve is closed when the coil is not energized, and the normally open type means that the valve is open when the coil is not energized.
2.5 Classification According to Internal Structure
Solenoid valves can be divided into two-position two-way valves, two-position three-way valves, two-position four-way valves, two-position five-way valves, etc. according to their internal structures.
2.6 Classification by Materials Used
Solenoid valves can be divided into cast iron body (gray cast iron, ductile iron), copper body (cast copper, forged copper), cast steel body, all stainless steel body (304, 316), and non-metallic material type (ABS, polytetrafluoroethylene) according to the material of the valve body.
2.7 Classification According to Medium Pressure in the Pipeline
Solenoid valves can be divided into: vacuum type (-0.1~0MPa), low pressure type (0~0.8MPa), medium pressure type (1.0~2.5MPa), high pressure type (4.0~6.4MPa), and ultra-high pressure type (10~21MPa) according to the medium pressure in the pipeline.

2.8 Classification According to Medium Temperature
According to the medium temperature, solenoid valves can be divided into:
1. Low temperature type (-40 to -20°C).
2. Ultra-low temperature type (below -40°C).
3. Normal temperature type (-5 to 80°C).
4. Medium temperature type (120 to 200°C).
5. High temperature type (250 to 400°C).
6. Ultra-high temperature type (higher than 400°C).
2.9 Classification According to Working Voltage
Solenoid valves can be divided into AC voltage type and DC voltage type according to the working voltage. The AC voltage type is divided into AC 24V, AC 110V, AC 220V and AC 380V according to the power supply voltage. DC voltage type is divided into DC 6V, DC 12V, DC 24V and other types according to the power supply voltage.
2.10 Classification According to Protection Levels
Solenoid valves can be divided into explosion-proof, waterproof, outdoor and other types according to the protection level.


