
Figure 1: Stepper motor.
Like servo motors, stepper motors are equipped with mechanisms that control the angle of rotation by receiving external signals. They can all perform operations such as positioning of equipment. However, when we choose a positioning mechanism, we do not understand the difference between stepper motors and servo motors clearly. In this article, we have made a detailed comparison between stepper motors and servo motors (servo motor vs stepper motor) and hope this will help you.
Only by understanding the difference between a stepper motor and a servo motor can we accurately determine whether to use a stepper motor or a servo motor.
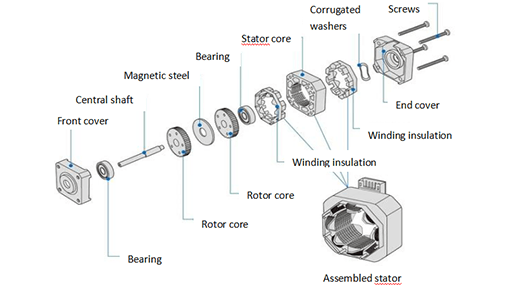
Figure 2: Stepper motor structure diagram.

Figure 3: Servo motor structure diagram.
1.Control Method
The servo motor detects the rotational position through the encoder (rotation detector), and feeds back the information detected by the encoder to the controller to control the position. Therefore, high-precision stop can be achieved, and even if it is stopped during rotation, it can return to the original position if the position deviates.

Figure 4: Working process diagram of servo motor.
The rotation angle of the stepper motor is proportional to the number of pulses, and the driver controls the position by receiving this pulse signal from the controller. Therefore, in fact, it does not need a mechanism for detecting the position, and it cannot recognize the deviation of the position. Therefore, losing step (a state in which the indicated rotation angle is not synchronized with the motor rotation) may occur due to reasons like unexpected load fluctuations.
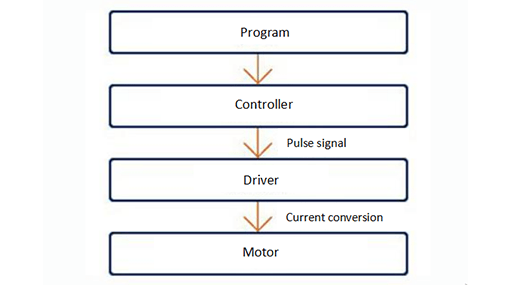
Figure 5: Working process diagram of stepper motor.
2.Control Precision
The servo motor is mainly composed of three parts, namely the motor body, the servo driver and the encoder. Its control accuracy is guaranteed by the rotary encoder at the rear end of the motor shaft.
What is the encoder for? In simple terms, it is used for error correction. It will compare whether the pulse signal received by the servo motor is consistent with the released pulse signal. If they are inconsistent, it will make them consistent, so that the motor will work strictly according to the instructions of the controller. That is, the motion of the servo motor is a closed-loop motion.
The accuracy of the stepper motor is generally decided by the precise control of the step angle. The step angle has a variety of different subdivision steps, which can achieve precise control. Since there is no such structure as an encoder, no one knows how well the stepper motor will do after receiving the command signal, so the control accuracy cannot be guaranteed.
Generally, the control accuracy of servo motors is higher than that of stepper motors. If your project pursues the ultimate precision, it is recommended that you use a servo motor.
3.Running Performance
Stepper motors are generally open-loop controlled. When the starting frequency is too high or the load is too large, there will be losing step or locked-rotor phenomena. Therefore, it is necessary to deal with the speed problem or add the encoder closed-loop control when using it.
The servo motor adopts closed-loop control, which is easier to control, and there is no phenomenon of losing steps.
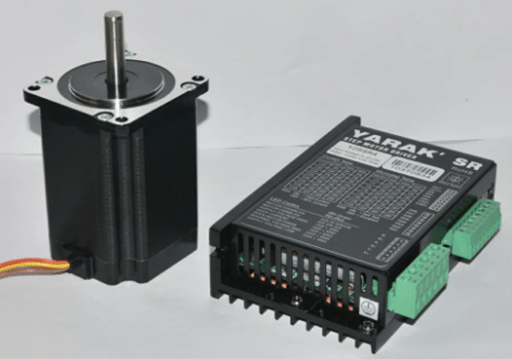
Figure 6: Stepper motor and stepper driver.
4.Torque/RPM
Servo motors can generate stable torque in both low-speed and high-speed ranges, so high-speed operation is possible.
Stepper motors can only generate high torque in the low-speed range, and the torque decreases in the high-speed range, so they are not suitable for high-speed rotation applications.
5.Low Frequency Characteristics
The stepper motor is prone to low frequency vibration at low speed. The vibration frequency is related to the load condition and the performance of the driver, and it is generally considered that the vibration frequency is half of the no-load starting frequency of the motor. This low-frequency vibration phenomenon determined by the working principle of the stepping motor is very detrimental to the normal operation of the machine.
When the stepper motor works at low speed, damping technology should generally be used to overcome the low frequency vibration phenomenon, such as adding a damper to the motor, or using microstepping technology on the driver.
The AC servo motor runs very smoothly and does not vibrate even at low speeds. The AC servo system has the function of resonance suppression, which can offset the lack of rigidity of the machine, and has a frequency analysis function (FFT) inside the system, which can detect the resonance point of the machine and facilitate the system adjustment.
6.Torque Frequency Characteristics
The output torque of the stepper motor decreases with the increase of the speed, and will drop sharply at a higher speed, so its maximum working speed is generally 300-600RPM.
The AC servo motor has a constant torque output, that is, within its rated speed (generally 2000 RPM or 3000 RPM), it can output the rated torque, and above the rated speed, it is a constant power output.
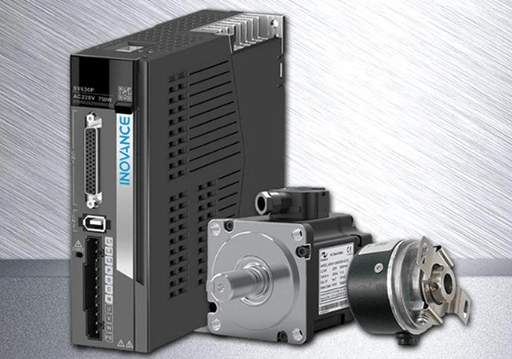
Figure 7: Inovance servo drive and servo motor.
7.Speed Response Performance
It takes 200 to 400 milliseconds for a stepper motor to accelerate from a standstill to a working speed (usually several hundred revolutions per minute).
The acceleration performance of the AC servo system is good. Taking the Panasonic MSMA400W AC servo motor as an example, it only takes a few milliseconds to accelerate from a standstill to its rated speed of 3000RPM, which can be used for control occasions requiring rapid start and stop.
8.Overload Capacity
Stepper motors generally do not have overload capability while AC servo motors have strong overload capacity.
Take the Panasonic AC servo system as an example, it has speed overload and torque overload capabilities. Its maximum torque is three times the rated torque, which can be used to overcome the moment of inertia of inertial load at the moment of starting.
Because the stepping motor does not have such overload capacity, in order to overcome the moment of inertia, it is often necessary to select a motor with a larger torque, while the machine does not need such a large torque during normal operation, so the wasteful phenomenon of torque appears.
9.Cost
Servo motors are more expensive than stepper motors because they need to use expensive rotary encoders and servo control devices (servo drives). Therefore, the stepper motor has an advantage in cost performance. The price of the servo motor is higher than that of the stepper motor of the same power to achieve the same function. The advantages of high response, high speed and high precision of the servo motor determine the high price of the product, which is inevitable.
Summary
The above is the difference between stepper motor and servo motor. Servo system is superior to the stepper motor in many aspects. So how to choose stepper motor and servo motor?
If the designed equipment requires fast speed, high precision, feedback on control, strong anti-overload capability, and multiple control modes, then choose servo. If the speed requirement is not high, no feedback signal is required, and the control is simple and convenient, then a stepper motor is recommended.
|
Comparison |
Stepper Motor |
Servo Motor |
|
Torque range |
Small and medium torque (generally below 20Nm) |
Small, medium and large, full range |
|
Speed range |
Low (generally below 2000 RPM, high torque motor less than 1000 RPM) |
High (up to 5000 RPM, DC servo motor up to 10,000 to 20,000 rpm)
|
|
Control method |
Mainly position control |
Diversified and intelligent control methods, position / torque / speed / bus control |
|
Smoothness |
Vibration at low speed, but can be significantly improved with microstep drives |
Good, smooth running |
|
Precision |
Generally lower (higher when using microstep drives) |
High (depending on the resolution of the feedback device) |
|
Torque frequency |
Torque drops quickly at high speed |
Good torque characteristics, constant torque output within the rated speed, and above the rated speed constant power output. |
|
Overload |
No overload capability, losing steps when overloaded |
3~10 times overload (short time) |
|
Feedback method |
Mostly open-loop control (can also be connected to encoder to prevent losing steps) |
Closed loop mode, encoder feedback |
|
Encoder type |
Photoelectric rotary encoder |
Incremental / absolute encoders, rotary transformer type, photoelectric rotary encoders |
|
Response time |
Average |
Quick |
|
Vibration resistant |
Good |
Average (rotary transformer type can withstand vibration) |
|
Temperature rise |
High operating temperature |
Average |
|
Maintainability |
Basically maintenance free |
Better |
|
Price |
Lower |
Higher |
Table 1: Stepper motor vs servo.
Related Info
AC Motor: Types, Speed Control, Features & UsesStepper Motor: Working Principle, Operating Modes & Application
Types of Stepper Motors: Three Methods to Classify
Types of DC Motors
Permanent Magnet DC Motor: Types, Application, Selection Principle (1)


