Priming a piston pump is probably the first and one of the most important thing one should do before operating it. Not priming a pump or not doing it properly makes majority of pump problems. Any problem in pump due to lack of priming may cause financial impact due to pump maintenance and the downtime of piping system due to a malfunctioning pump.

Figure 1: Priming in pumps.
1. What it is
Pump Priming is the process of removing air from the pump and suction line. In this process the pump is been filled with the liquid being pumped and this liquid forces all the air, gas, or vapor contained in the passage ways of pump to escape out. Priming maybe done manually or automatically. Not all pumps require priming but mostly do. There are Self Priming Pumps and also some layout situations where priming is not required.
2. Methods of Priming
Priming of a pump can be achieved by either layout consideration, or by means of some external arrangements that ensures priming or by use of Self Priming Pumps. Few of the external arrangements that ensures priming of a pump are detailed out below.
2.1Manual Priming
In this method of pump priming, liquid is poured in the pump suction. This can be achieved by pouring liquid directly in suction or with the help of other devices like a funnel and the pump will be manually primed with a gravity feed. While priming is being done, all the air escapes through air vent valve.
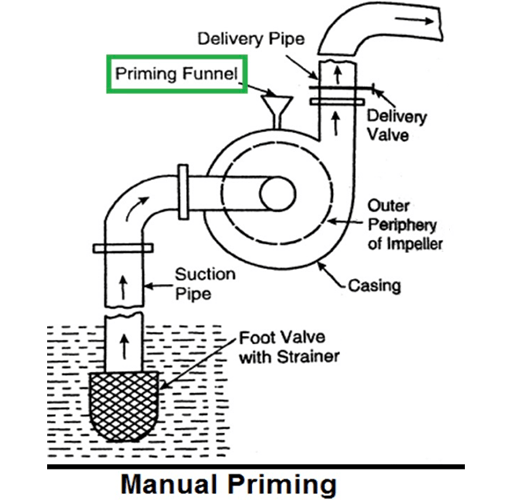
Figure 2: Manual priming.
2.2 Priming with Vacuum Pump
In this method of pump priming, a small size vacuum pump or self priming pump or a positive displacement pump is being used for priming the main centrifugal pump. The suction line of positive displacement pump is connected to the discharge line of main centrifugal pump. This positive displacement priming pump evacuate all the air in the primary pump and suction piping.
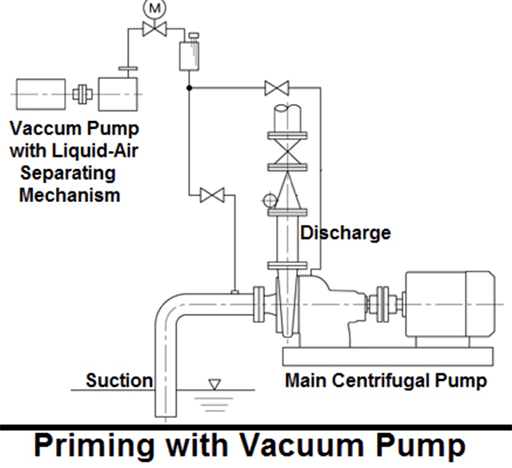
Figure 3: Priming with vacuum pump.
2.3 Priming with Jet Pump
In this method of pump priming, water available at high head is allowed to flow through a nozzle. The nozzle is so designed that at the jet outside the nozzle the pressure is less than the atmospheric pressure so it is possible to suck water from the sump.
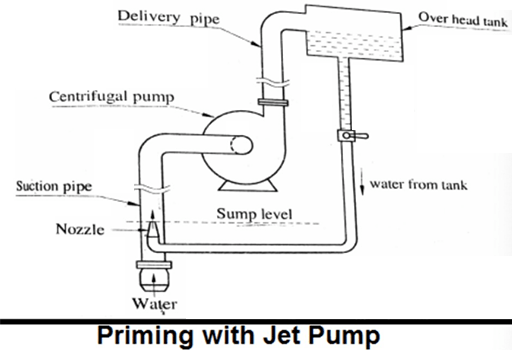
Figure 4: Priming with jet pump.
2.4 Priming with Ejector
In this method of pump priming, ejector is provided on the suction side of pump. Ejectors operate by creating a vacuum inside the suction line of the pump. The vacuum draws the liquids from sump up to the pump elevation. Ejectors require a Compressed Air Supply as an energy input.

Figure 5: Priming with ejector.
2.5 Priming by Installing Foot Valve
In this method of pump priming, a foot valve (functioning as a NRV) is installed in the suction piping to insure that the liquid will not drain from the pump casing and suction piping once the pump stops operating. A foot valve is a form of check valve installed at the bottom, or foot, of a suction line. When the pump stops and the ports of the foot valve close, the liquid cannot drain back from pump suction if the valve seats tightly. Keep in mind that these foot valves have a nasty habit of leaking.
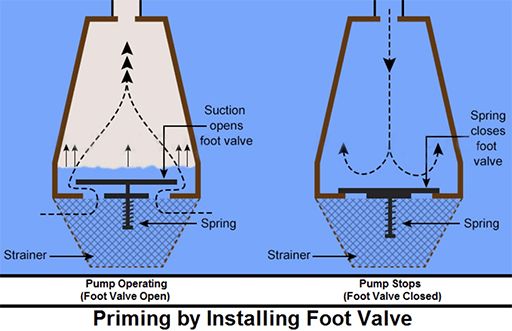
Figure 6: Priming by installing foot valve.
3. Prevention of Pump Operation without Priming
For prevention of a pump, where priming is required, operation without being primed various methods are being used. The basic of these methods are to trigger some form of alarm or auto shutdown of pump if the pump is not filled with liquid completely.
In some pumps, a form of float switch in a chamber connected with the suction line is being used. If the level in the chamber is above the impeller eye of the pump, the float switch control allows the pump to operate. If the liquid falls below a safe level, the float switch acts through the control to stop the pump, to prevent its being started, to sound an alarm, or to light a warning lamp.
Related Info
What is Piston Pump?6 Common Faults of Encoder?
Different Types of Encoder and Their Differences?
Applications of Encoder
How to Test an Encoder with a Digital Multimeter?


