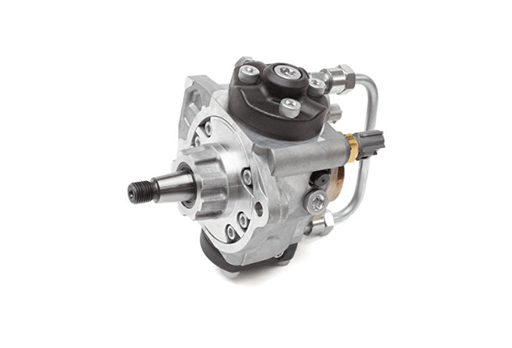
Figure 1: A piston pump laid on the desk.
1. Definition
A piston pump is a type of positive displacement pump where the high-pressure seal reciprocates with the piston.Piston pumps can be used to move liquids or compress gases. They can operate over a wide range of pressures. High pressure operation can be achieved without adversely affecting flow rate. Piston pumps can also deal with viscous media and media containing solid particles.This pump type functions through a piston cup, oscillation mechanism where down-strokes cause pressure differentials, filling of pump chambers, where up-stroke forces the pump fluid out for use. Piston pumps are often used in scenarios requiring high, consistent pressure and in water irrigation or delivery systems.
2. Working Process
Piston pumps are designed to control the flow of fluid. Many of these pumps are part of hydraulic systems designed to produce energy. Once a pump is activated, the resulting pressure moves the hydraulic fluid and powers a mechanism.

Figure 2: Working process of a piston pump.
These systems are incredibly powerful. A leading piston pump is capable of delivering as much as 10,000 pounds per square inch of differential pressure. This allows even the heaviest equipment to operate buckets, lifts, drills and other equipment.
The exact process is determined by the type of pump. There are five basic types of hydraulic piston pumps, and each one is used in a slightly different way to direct and control the flow of fluid. Compare these types of pumps to determine the best option for your equipment needs.
3. Common Piston Pump Types
Depending on the amount of pressure, size of equipment and other considerations, manufacturers choose one of these five types of piston pumps. Be sure to check the type of pump in your equipment for hassle-free replacement: Axial pump, Bent axis pump, Inline pump and Plunger pump.
3.1 Axial Pump
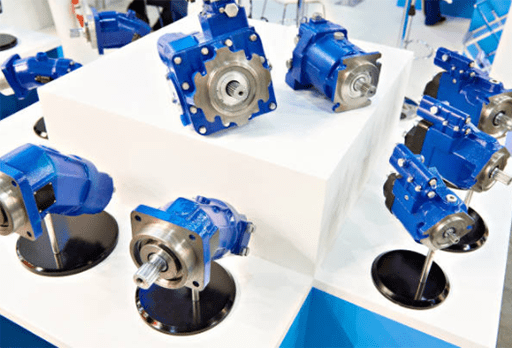
Figure 3: Axial pumps.
An axial pump uses a propeller to push fluid along the axis in a spiral motion. These unique pumps are common in aerospace and marine applications, including jet and torpedo use. They stand up well in high-temperature situations and can produce a particularly high flow of hydraulic fluid.
3.2 Bent Axis Pump

Figure 4: Bent Axis pump.
A bent axis piston pump can bend up to 40 degrees and still spin effectively. Compared to inline pumps, this type allows far more flexibility and higher spin rates.
3.3 Inline Pump
Figure 5: Inline pumps.
One of the most common types of pumps is an inline axial piston pump. This type is ideal for water pressurization and is a very efficient option. It doesn’t have the same flexibility as a bent axis pump but is capable of some levels of flexible performance.
3.4 Plunger Pump

Figure 6: Plunger pump.
Finally, a plunger piston piston pump uses a cylindrical shape to displace fluid. The back-and-forth motion of a plunger allows it to produce reliable energy with minimal maintenance. These pumps are commonly used in pressure washing and reverse osmosis projects.
Related Info
What is an Encoder?6 Common Faults of Encoder?
Different Types of Encoder and Their Differences?
Applications of Encoder
How to Test an Encoder with a Digital Multimeter?


