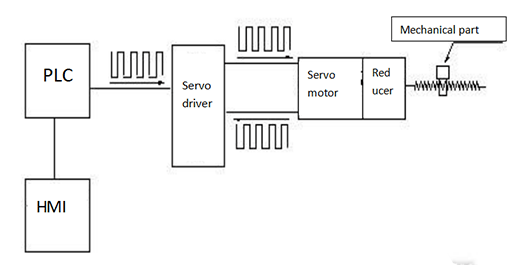
Figure 1: Servo system diagram.
This article introduces the basic knowledge, working principle, selection and related FAQs of servo motors.
What is Servo Motor
The control system of the servo motor can control the motor to rotate to an accurate position, and make the corresponding rotation action at any time as needed.
Servo motors are used as executive elements in automatic control systems to convert received electrical signals into angular displacement or angular velocity output on the motor shaft.
During the rotation of the servo motor, there will be components to identify the angle and direction that the motor has turned, and feed this signal back to the control system, so that the control system can identify whether the motor is rotating in place, and then control the motor to make corresponding actions (continuing to rotate, stop or reverse).
The main feature of the servo motor is that when the signal voltage is zero, there is no self-rotation phenomenon, and the speed decreases uniformly with the increase of torque.
How Does a Servo Motor Work
The servo system is an automatic control system that enables the output controlled quantities such as the position, orientation, and state of the object to follow the arbitrary changes of the input target (or given value).
The servo mainly relies on pulses for positioning. When the servo motor receives 1 pulse, it will rotate the angle corresponding to 1 pulse to realize displacement. Because the servo motor itself has the function of sending out pulses, it will send out the corresponding number of pulses for each angle of rotation.
In this way, a closed loop is formed, and the system will know how many pulses are sent to the servo motor and how many pulses are received at the same time. Therefore, the rotation of the motor can be precisely controlled, so as to achieve precise positioning (accuracy up to 0.001mm).
How to Select A Servo Motor
The following below lists 9 steps of servo motor selection, hoping to provide some help to those who need it.
STEP 1: Determine the mechanical installation structure.
|
Content |
|
|
Control |
l Multi-axis synchronization l Single shaft drive |
|
Installation type |
l Vertical? l Horizontal? |
|
Mechanical type |
l Is there a reduction mechanism? l Type of output shaft on the drive side, keyway? Plain shaft? l Are there flanges? l Is there a holding brake? l Vibration level? |
|
Motion type |
l Horizontal linear motion? l Rotational motion? |
|
Installation size |
l Structural size requirements |
Table 1: Servo motor installation type.
STEP 2: Requirements on environmental conditions.
|
Content |
|
|
Ambient temperature |
l Standard operating conditions |
|
Environment humidity |
l Standard operating conditions |
|
Protection class |
l Dust requirements l Waterproof requirements |
|
Explosion-proof requirements |
l Gas Zone 2 Explosion Proof l Dust zone 22 explosion-proof |
Table 2: Environmental conditions required by servo motors.
STEP 3: Load characteristics.
|
Content |
|
|
Work method |
l S1 (continuous ) l S6 (intermittent ) l Duty cycle l Overload requirement |
|
Load type |
l Passive load l Active load |
|
Output torque |
l Output torque requirement l Output speed range requirement |
Table 3: Load characteristics of servo motors.
STEP 4: Requirements on environmental conditions.
|
Content |
|
|
Control mode |
l Servo mode l Vector mode l V/f mode |
|
Process control |
l Position control l Speed control l Torque control |
|
Output performance |
l Speed regulation range l Steady-state accuracy l Dynamic response characteristics, moment of inertia, acceleration and deceleration time, etc. |
Table 4: Control method selection of servo motor.
STEP 5: Servo motor selection. Please refer to the selection manual of the servo motor manufacturer, and select the corresponding servo motor in combination with STEP 1~4.
STEP 6: Select the encoder system according to the actual application requirements.
STEP 7: After basically determining the servo motor, select the servo driver recommended in the manufacturer's selection table.

Figure 2: SINAMICS drive systems and SIMOTICS motor.
STEP 8: Select the controller of the servo drive system.
|
Content |
|
|
Controller |
l Machine tool controller SINUMERIC l SIMOTION l CU320/CU310 etc. |
|
Interface type |
l PROFIBUS DP l PROFINET, etc. |
|
Encoder interface |
l DRIVE-CLiQ interface l SMx interface, etc. |
Table 5: Controller selection of servo drive system.
STEP 9: Cable selection.
|
Content |
|
|
Power cable |
l Determine the servo motor l Recommended power cable models in the selection table |
|
Signal cable |
l Determine the servo motor l Recommended signal cable types in the selection manual |
Table 6: Cable selection of servo motor.
FQAs
1.Why is it called a servo motor?
The servo motor is named because of its "servo" performance, which can accurately perform the requirements of the control signal. Before the signal comes, the rotor is stationary; after the signal comes, the rotor turns immediately; when the signal disappears, the rotor can immediately stop.
The main task of the servo is to amplify, transform and regulate the power according to the requirements of the control command, so that the torque, speed and position of the drive output can be controlled very flexibly and conveniently.
2.Are servo motors AC or DC?
Servo motors are divided into two categories: DC and AC servo motors.
DC servo motors are divided into brushed and brushless motors.
AC servo motors are also brushless motors, which are divided into synchronous and asynchronous motors. Synchronous motors are generally used in motion control, which have a large power range and can achieve a great power.

Figure 3: Types of servo motor.
3. How to troubleshoot the servo motor overheating?
1) Overcurrent. It may be due to the wrong setting of the overcurrent protection value of the driver or the shielding of the overcurrent protection function. You can check the relevant settings. In addition, you may need to check whether the motor bearing is normal, whether the three-phase power supply terminals of the motor are firmly connected, whether the three-phase current is unbalanced, and whether the rotation direction of the motor changes too quickly.
2)Faulty motor cooling system. If the heat generated by the motor cannot be dissipated as soon as possible, the motor temperature will rise too high. The main solution is to check whether the motor cooling fan is running normally, whether the fan rotates in the right direction or not, whether the cooling duct is blocked, whether the motor body has sludge, oil pollution and other debris accumulation that affects heat dissipation, etc.
3)The temperature measurement value is wrong or inaccurate. Please measure it with a standard temperature detection instrument to see if there is a big difference between the measured value and the value displayed by the driver.
If the measured value is consistent with the displayed value or there is a subtle difference between them, it proves that the displayed value is correct and the temperature of the motor temperature sensor is normal. If the difference between the measured value and the displayed value is large, it is likely that the motor temperature sensor is faulty.
All in all, if the alarm parameter value of the driver is set incorrectly or unreasonably, it must be corrected, otherwise the motor will be damaged over time.
4. What is the difference between AC servo motor and brushless DC servo motor in performance?
The performance of the AC servo motor is better, because the AC servo is controlled by a sine wave, and the torque ripple is small, while the brushless DC servo is controlled by a trapezoidal wave. But brushless DC servo control is relatively simple and cheap.
The AC servo system has become the main development direction of the contemporary high-performance servo system, which makes the DC servo system face the crisis of being eliminated.
As a professional supplier of industrial parts, Okmarts has deep cooperation with many China servo motor manufacturers as well as foreign manufacturers, and we can provide you with various servo motors, such as smart servo motors, integrated servo motors, etc.
Related Info
What is a Hydraulic Vane Pump?How to Choose a Gear Pump?
What is Positive Displacement Pump?
Positive Displacement Pump vs Centrifugal Pump
What is the Difference Between Piston and Plunger Pumps


