Video: Printer Cooling: Methods, Common Problems & Troubleshooting

Figure 1: Office copying machine.
Printers are familiar to everyone and are one of the essential office tools for work. From inkjet, dot matrix,
laser, to the now popular 3D technology, printers have developed rapidly. While performance is gradually improving,
prices are also decreasing, making office work more convenient.
3D printing technology is still some distance away from us, and we are most exposed to printers used in daily office
work. Careful friends will also notice that after the printer has been working for a long time, the printing
efficiency is significantly reduced, and the printer body is easy to get hot. In an emergency, it may even have to
be shut down and stopped for a while to restore the printing speed.
There are many factors that will directly affect printer's working efficiency: temperature, hardware aging, and
working hours. The usual approach is to replace old parts, wipe the body to speed up heat dissipation, and turn it
off at any time when not in use.
These methods are useful to solve small printer problems, but not suitable for some large printers. On the one hand,
large printers should always be available when needed; on the other hand, large printers dissipate large amounts of
heat, making maintenance inconvenient and costly.
1. Printers Can Also Use Water-Cooling Method
Currently, the mainstream printer cooling method is fan cooling,
which is low-cost and widely used. But there are also some problems such as poor heat dissipation and high noise.
Nowadays, water-cooling, which is hot in the computer DIY market, can also be used for printer heat dissipation.
After years of market use, it has been proven that water-cooling heat dissipation is quiet and efficient, which can
ensure that the printer works for a long time without reducing efficiency.
When it comes to water-cooling heat dissipation, many people are confused. In fact, the principle of water-cooling
heat dissipation is very simple.
The water-cooling block is closely connected to the heating core, and the water pump and radiator are connected
through water pipes to form a complete water cycle. Then the heat is carried away by the flowing liquid. If adopting
this method, there is no need to worry about the printer overheating.
Industrial printers have greater demand for heat dissipation, and can also use water-cooled heat dissipation.
Water cooling can be said to be a new revolution in printer heat dissipation. Although it is only used on a small
scale, its application prospects are unlimited. With the popularization of heat dissipation technology, it will
definitely be used more in production and life.

Figure 2: Water cooling printer.
2. What to Do If the Printer Emits Steam or Moisture When Printing
It is normal for printers to generate heat during operation, and most printers have built-in heat dissipation systems to keep the printer's temperature within a safe range. However, if we notice that our printer is steaming, why and what to do?
2.1 Paper Gets Damp
During the printing process, if the printer emits "steam" and has no peculiar smell, it can be confirmed that there
is no problem with the printer hardware and it can be used normally.
The printer's heating component uses instantaneous heating technology, and the working temperature is relatively
high. If the paper gets damp, the heat and water vapor generated during the printing process will be discharged
through the exhaust holes, so "steam" will appear. This phenomenon often occurs when the air temperature is low and
the humidity is high.
Usually there will be leftover paper in the printer. If the paper gets damp, dry it before printing.
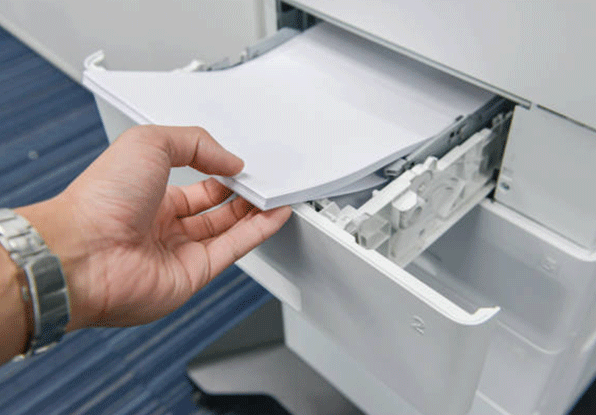

Figure 3: Reload the paper at the printer tray.
3. How to Fix the Heat Dissipation Problem of Laser Printer?
Laser printer is one of the essential tools in the modern office. Due to its high efficiency and high precision, heat dissipation problems may occur during long-term use, which is also a common problem. If you encounter a laser printer heat dissipation problem, how should you solve it?
3.1 Clean the Dust
When a laser printer is used for a long time, it is easy for dust to accumulate in the heat dissipation holes, fans,
etc., causing the body to get hotter and hotter.
Therefore, the dust should be cleaned first. You can use an eraser, hair dryer, etc. to clean up the dust.
3.2 Replace the Cooling Fan
If you still have cooling problems after cleaning, the cause is most likely due to a problem with the fan.
At this time, the cooling fan needs to be replaced. It should be noted that when replacing, you should choose a fan
that is the same as the original fan model, otherwise it will not work properly.

Figure 4: Laser printer fan.
3.3 Pay Attention to Surroundings
When using the printer, attention should be paid to environmental temperature control. If the ambient temperature is
too high, it will affect the normal heat dissipation of the printer and cause failure.
Therefore, the room temperature should be kept at around 20°C and avoid blowing the printer directly with cold air.
3.4 Replace the Heat Sink
If the previous operations have no effect, then there is most likely a problem with the heat sink. In this case,
only the heat sink can be replaced.
It should be noted that when replacing the heat sink, you should choose the same model and specifications as the
original heat sink.
In short, if you encounter a laser printer heat dissipation problem, you should first clean up the dust and maintain
a suitable ambient temperature. If that doesn't work, you need to consider replacing the cooling fan or heat sink.
By following these methods, I believe your laser printer will return to normal.
4. What to Do If the Printer Does Not Print (Overheated Printer)?
In the process of using the printer, we may encounter a situation that the printer does not print. Many people will
think that the printer is malfunctioning. In fact, not all printer failures require repair, and some problems can be
fixed through simple steps.
Next, let's take a look at the reasons and solutions for why the printer won’t print.
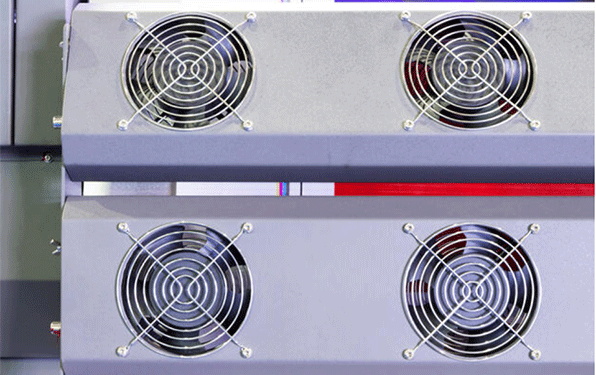
Figure 5: Cooling fans in an industrial printer.
4.1 Reason: Hot Printer
There are many reasons why a printer may not print, but the most common one is that the machine heats up. Printers tend to heat up during long-term use. If the machine heats up excessively, the printer may not work properly and may be printing blank pages or unable to print.
4.2 Solution 1: Clean the Printer
Cleaning the print head and nozzles is one of the most basic ways to solve the problem of printer heating. Because
the printer will produce a lot of waste and dirt during operation, if it is not cleaned in time, it will affect the
performance of the printer and cause heating problems.
Use a cleaning stick or clean cotton cloth to wipe the nozzle and print head to effectively remove dirt and waste.
At the same time, you can also clean the casing and air inlet to keep the printer clean and tidy and reduce the
occurrence of heating problems.
4.3 Solution 2: Heat Dissipation
The problem of printer heating can also be solved by adding heat dissipation measures. Most printers have cooling
fans, and if the fans are old or clogged, they can cause heating problems. Therefore, you can clean or replace the
fan to increase the heat dissipation effect and solve the problem of machine heating.
In addition, you can also place the printer in a ventilated place to allow it to dissipate heat automatically. When
the printer is under high workload, you can install a fan or heat sink on the printer to improve the heat
dissipation effect and avoid overheating of the machine.
5. Conclusion
If we find that the printer is abnormally hot, we should take measures to solve it as soon as possible. This can not
only extend the service life of the printer, but also avoid printer failure.
As users, we should pay attention to the daily maintenance and upkeep of the printer to avoid excessive wear and
damage to the printer during use. At the same time, timely handling of printer failures and problems can improve
office efficiency and reduce the company's operating costs.



