
Figure 1: Solenoid valve and solenoid coil.
(Go to Okmarts and pick the Solenoid Coil you need)
The solenoid valve coil generates a magnetic field. This moves a ferromagnetic plunger inside the valve which opens or closes the valve. When a coil (solenoid) is defective, it can be difficult to find a replacement for the original. A universal replacement coil can be a solution. This article lists the most important parameters that you should take into account to make an informed choice.
1. Determine The Dimensions And Fixation of The Coil
One of the most important aspects in the selection of a replacement coil, is that the dimensions of the hole correspond with the original coil (diameter D and height H). The replacement coil may have a small clearance in the diameter, but not too large. The field strength decreases as the gap increases. As an rule of thumb, you can take a maximum tolerance of 15% of the armature diameter. Often coils are fixed by means of a nut.

Figure 2: The diameter and height of the hole in the coil.
2. Determine The Voltage And Electrical Power
2.1 Voltage And Type of Signal (AC or DC)
Determine whether the electrical connection is AC or DC. AC stands for Alternating Current, DC for Direct Current. AC is sometimes indicated with the frequency of the voltage signal in Herz (Hz), for example, 50Hz or 60Hz. Sometimes a symbol is used.
Typical voltages are 230V AC, 120V AC, 24V AC, 24V DC or 12V DC. If you are not certain about the voltage and the type of signal (AC / DC), it is a good idea to check the power supply using a multimeter.
2.2 Electric Power (Watts)
The electric power of a coil is the amount of electrical energy that is dissipated (used) is used as it is mounted on the solenoid valve, and is turned on. This is usually expressed in units of watts (W). Make sure that the capacity of the replacement spool is approximately equal to, or higher than, the value of the defective coil.
For DC current, the electrical power is linearly dependent on the voltage and amperage according to the formula:
P=V·I
P = electrical power in watts (W)
V = voltage in volts (V)
I = amperage in Ampere (A)
If two of the three variables are known, the third is easy to calculate. To illustrate, we calculate the amperage of a 12V DC coil with an power of 6 watts. I = P / V or 6/12 = 0.5 Amps.
For AC this formula doesnt apply, because the voltage signal is a sinusoidal motion. The actual power may be determined with a correction factor, the socalled power factor. In practice, the actual power will be slightly lower than Volts x Amps.
3. Determine The Type of Connector
Solenoid valve coils are often offered with a DIN connector. The coil is carried out with pins that can be connected to a female connector. A DIN connector has clear advantages over wires, such as good insulation, moisture protection, and fast connection. The most common models are DIN43650-A and DIN43650-B. The dimensions of both variants are shown in the figure below.
 and DIN-B (right)-min.png)
Figure 3: Dimensions for DIN-A (left) and DIN-B (right).
4. Installation
Before starting the installation, you should have read the safety instructions. Attach the coil on the solenoid valve according to the example drawing. If you are using AC, it is very important that the coil is not energized when it is not mounted onto the solenoid valve. Due to the lack of mass in the coil core, the current increases and as a result, the coil may burn.
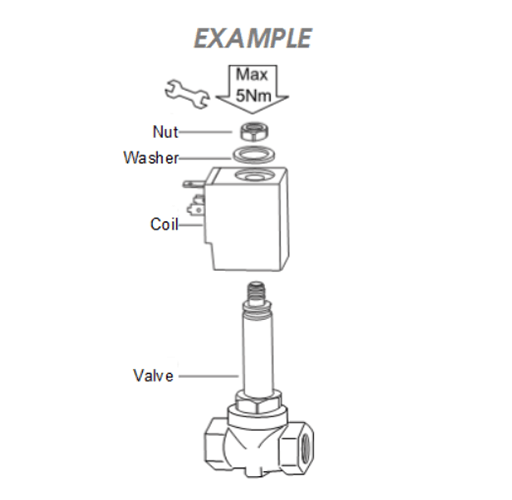
Figure 4: Installation of a DIN connector for solenoid valves.
If the coil has a DIN connector, the figure below can be used as a guidance. Connect the terminals 1 and 2 to the power supply. Polarity is not important. Always connect the earth, never use the pipe itself as earthing. Connect the connector in such a way that moisture cannot enter. Use a round cable and make sure that drops on the cable cannot slip into the connector.
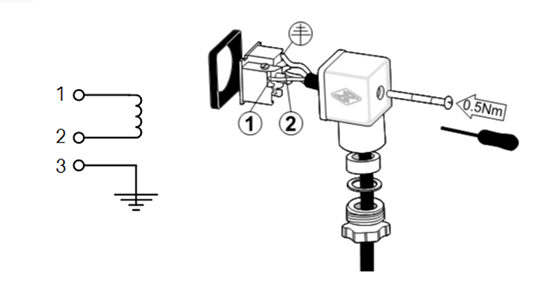
Figure 5: Installation of a DIN connector for solenoid valves.
Related Info
What is A Solenoid Coil?Function and 7 Common Types of Solenoid Coil?
What is Power Supply?
6 Common Types of Power Supply


