
Figure 1: Centrifugal fan vs axial fan.
Centrifugal fans and axial fans are two common types of fan systems used in various
industries and applications. While both are designed to move air or gases, they differ in their construction,
airflow characteristics, and performance.
In this article, we will explore the distinctions between centrifugal fans and axial fans, their working principles,
and the applications where each type excels.
1. Centrifugal Fans
Centrifugal fans, also known as radial fans, use centrifugal force to generate airflow. They consist of a rotating
impeller with curved blades, housed within a scroll-shaped enclosure.
As the impeller spins, air enters through the center and is accelerated radially outward towards the scroll,
creating pressure. The air is then expelled tangentially from the fan outlet.

Figure 2: The airflow direction of a centrifugal fan (Image from CUI Devices).
1.1 Key Features and Advantages of Centrifugal Fans
a) Increased Static Pressure: Centrifugal fans are excellent at generating higher static pressures, making them
suitable for applications that require airflow resistance, such as ventilation systems, HVAC systems, and industrial
processes.
b) Versatile Design: Centrifugal fans can handle a wide range of airflow volumes and pressure requirements,
accommodating various system configurations and ductwork layouts.
c) Efficient Airflow Direction Changes: The curved blades of centrifugal fans allow for efficient redirection of
airflow, making them effective in applications that involve complex air circulation patterns or confined spaces.
2. Axial Fans
Axial fans, also known as propeller fans, create airflow by using the axial direction, parallel to the fan's axis of
rotation. They consist of a hub with multiple axial blades that rotate within a cylindrical or panel-shaped housing.
Air enters parallel to the fan's axis and is propelled axially, flowing straight through the blades and out of the
fan.
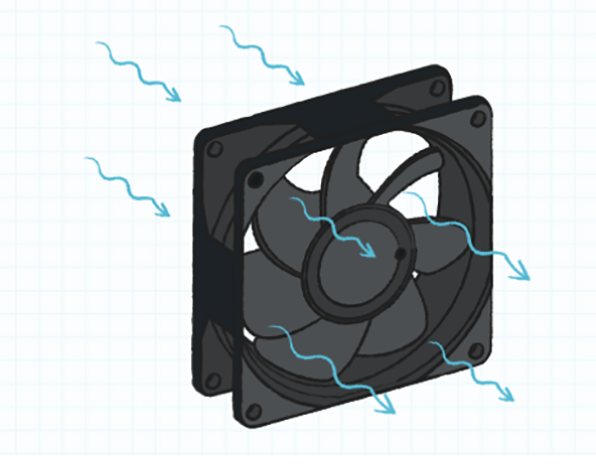
Figure 3: The airflow direction of an axial fan (Image from CUI Devices).
2.1 Key Features and Advantages of Axial Fans
a) High Airflow Volume: Axial fans are capable of generating high airflow volumes, making them ideal for
applications that require moving large amounts of air, such as cooling large equipment, air circulation in
warehouses, or ventilation in industrial facilities.
b) Lower Pressure Generation: Although axial fans do not generate high static pressures like centrifugal fans, they
are efficient at producing a steady flow of air, especially when the resistance to airflow is relatively low.
c) Energy Efficiency: Axial fans are known for their energy efficiency, consuming less power compared to centrifugal
fans at similar airflow rates. This efficiency makes them cost-effective for applications that prioritize energy
savings.
3. Applications and Usage Scenarios
3.1 Centrifugal Fans
Centrifugal fans are commonly employed in various applications that require high static pressures, including:
1.HVAC systems: Centrifugal fans provide effective air distribution and ventilation in residential, commercial, and
industrial buildings.
2. Industrial processes: They are used for drying, cooling, dust collection, combustion air supply, and pneumatic
conveying in manufacturing facilities.
3. Air handling units: Centrifugal fans assist in maintaining air quality and temperature regulation in HVAC
equipment.
3.2 Axial Fans

Figure 4: Axial fan.
Axial fans find application in scenarios that involve high airflow volumes, such as:
1. Cooling and ventilation: Axial fans are used in cooling towers, heat exchangers, condensers, and air-cooled heat
sinks to dissipate heat.
2. Data centers: They aid in cooling server racks and computer equipment to prevent overheating.
3. Agricultural and horticultural industries: Axial fans are used in greenhouses, barns, and agricultural facilities
to maintain ventilation and control temperature.
4. Comparing Axial Fans and Centrifugal Fans on Different Aspects

Table 1. Axial vs centrifugal fan.
5. FAQs
5.1 Is Axial or Centrifugal Fan Better?
Determining whether an axial or centrifugal fan is better depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Axial fans are better suited for applications that prioritize high airflow volumes with relatively low resistance to
airflow, such as cooling large equipment or ventilation in open spaces.
On the other hand, centrifugal fans are more suitable when higher static pressures are required, making them ideal
for HVAC systems, industrial processes, and applications with ductwork and airflow resistance.
Ultimately, the choice between axial and centrifugal fans depends on factors such as airflow needs, pressure
requirements, space limitations, and energy efficiency considerations.
5.2 What is the Advantage of Centrifugal Fan over Axial Fan?
The advantage of a centrifugal fan over an axial fan lies in its ability to generate higher static pressures.
Centrifugal fans are designed to produce a significant pressure increase, making them ideal for applications that
require air to be moved against resistance, such as ventilation systems, HVAC systems, and industrial processes.
This is achieved through the curved blades and scroll-shaped enclosure of the centrifugal fan, which efficiently
convert the rotational motion into a radial airflow.
In contrast, axial fans are more suitable for applications with lower resistance to airflow and where high airflow
volumes are required. Overall, the advantage of a centrifugal fan is its ability to deliver increased static
pressure, allowing for efficient air movement in challenging environments.
5.3 What are the Disadvantages of Axial Fans?
The primary disadvantage of axial fans is their limited capability to generate high static pressures. Axial fans are
more efficient at producing large volumes of airflow with low resistance, but they struggle to overcome higher
levels of static pressure. Additionally, axial fans tend to be less effective in applications that require airflow
redirection or circulation in confined spaces due to their straight-through airflow pattern.
Furthermore, compared to centrifugal fans, axial fans may not be as energy-efficient in certain scenarios,
especially when operating against higher resistances. It's important to consider these limitations when selecting
fan systems for applications that require high pressure generation or airflow direction changes.
5.4 What are the Advantages of Axial Fans?
The advantages of axial fans include their ability to generate high airflow volumes, their energy efficiency, and
their relatively lower cost compared to centrifugal fans. Axial fans are highly effective at moving large volumes of
air in applications where high static pressure is not a requirement.
They are widely used for cooling purposes, such as in cooling towers, heat exchangers, and air-cooled heat sinks.
Axial fans are also known for their energy efficiency, consuming less power than centrifugal fans at similar airflow
rates. Additionally, their simpler construction results in lower manufacturing and maintenance costs, making them a
cost-effective choice for many applications.
Conclusion
In summary, both centrifugal fans and axial fans have their respective strengths and applications. Centrifugal fans excel in generating higher static pressures and are ideal for applications involving airflow resistance. On the other hand, axial fans are known for their high airflow volumes and energy efficiency, making them suitable for applications that prioritize moving large volumes of air. Understanding the differences between these fan types helps in selecting the appropriate fan system based on the specific requirements of each application.


